Recommended Operating Tips for Robotic Welding Applications
Nozzles:
- If anti-spatter is used, do not use excessive spray times as this will saturate the nozzle insulator and will degrade insulating material. Learn more about TOUGH GARD® anti-spatter liquid from Tregaskiss.
- Nozzle should be cleaned as often as possible. Spatter buildup can often lead to poor gas shielding or short-circuiting between the contact tip and the nozzle.
- Spatter should be removed with the proper tools designed for spatter removal.
- In high temperature welding applications, heavy duty consumables are recommended.
Contact Tips, Retaining Heads, Gas Diffusers and Liners:
- TOUGH LOCK® contact tips may be removed and rotated 180° in retaining head / gas diffuser, providing an additional wear surface and extending the service life of the product.
- Inspect retaining head for spatter adhesion, blocked gas ports and carburized contact surfaces. Clean as often as possible.
- Ensure all consumables are tightly fastened and sized properly for your application.
- Do not immerse liner into solvents for cleaning. The liner may be periodically blown out with compressed air.
Necks:
- Use of a checking fixture is recommended to ensure a repeatable TCP.
- Ensure neck connections are properly torqued. Loose Connections = Resistance, and Resistance = Excessive Heat.
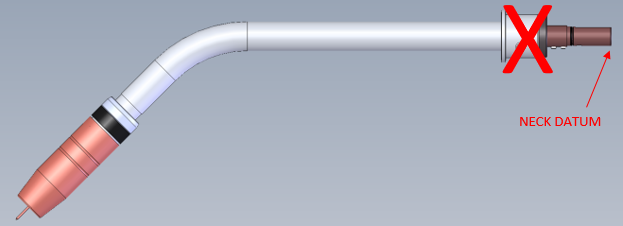
- As shown below, the neck datum is the back of the copper – not the torch body.
Gun Cables:
- Periodically check neck, cable, and power pin connections. Loose connections can cause overheating and premature failure.
- Sharp bends and loops in the cable should be avoided. You can suspend the wire feeder from a boom or trolley in semi-auto applications or use counterbalances in automation applications. This will help eliminate excessive bends and keep the cable clear of hot weldments.
- Avoid rough surfaces and sharp edges that can cause tears and nicks in cable jacket which can cause premature failure.
- Periodically check all ground cables and connections.
- Use anti-seize on all threaded connections.
- Ensure your cable is properly sized for the application, especially in automation. Excessive slack (more than ~3″) or overly-taught cables will lead to premature failure.
Reamers:
- Use the reamer to remove accumulated spatter as needed. TOUGH GARD anti-spatter liquid can be applied / sprayed at the same frequency as reamer cycles, or it can be applied independently between ream cycles.
- Reamer cycles can be “hidden” in table indexes or part loading to minimize downtime.
- Ensure the unit is supplied with 80-100 psi while under load to ensure optimal results.
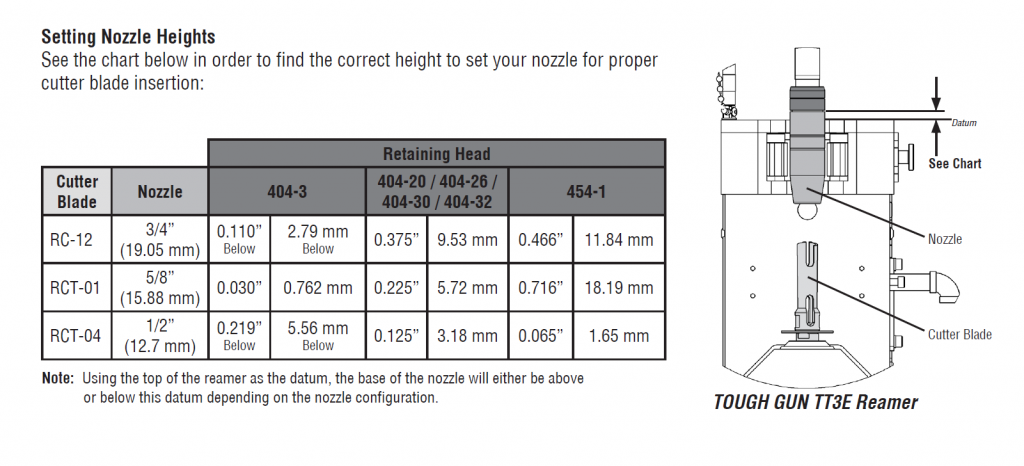
- Ensure the torch is programmed to the proper position. Access the TOUGH GUN Reamer Cutter Blade and V-Block Chart, and see the Setting Nozzle Heights chart below: